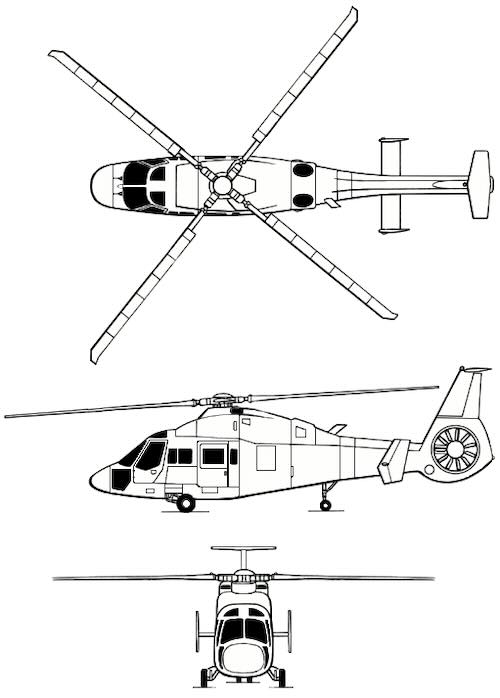
Ka-60 Kasatka
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇷🇺 Russia |
| Manufacturer | Kamov |
| First flight | 10 December 1998 |
| Year introduced | None |
| Number produced | 2 units |
Description
The development of the Ka-60 began in 1984. The initial prototype, Ka-60-01, made its first flight in December 1998, followed by a second prototype in 2007. An early civil version proposal, the Ka-62, faced hindrances in production due to development issues with the Ka-60's Saturn RD-600V engines.
In April 2011, an agreement led to the incorporation of the Turbomeca Ardiden 3G turboshaft for a revised Ka-62. This revision included a new transmission, an updated cabin with larger windows, and new avionics. Flight tests of this Ka-62 began in 2017. Following 434 test flights conducted over 700 hours, the aircraft was certified on 30 November 2021.
By late 2022, development and certification of the Ka-62 were halted. This cessation was attributed to Western sanctions and reliance on foreign-made components, including the French-manufactured engine.
The Ka-60 was designed for military roles, including aerial reconnaissance, transporting air-assault forces, radio-electronic jamming, special operations, and light-transport missions. The civil version, Ka-62, features a five-blade main rotor and a shrouded tail rotor. It can carry up to 15 passengers or between 2 and 2.5 tonnes of cargo.
Power for the Ka-62 is provided by a pair of Safran Ardiden 3Gs. Future models were planned to utilize the in-development Klimov VK-1600 engine. The Ka-62 also incorporates a 30-minute run-dry gearbox by Zoerkler and is designed for single-engine operation up to an altitude of 9,500 ft. The Ka-62 features a redesigned fuselage with a high degree of composite material usage and a larger cabin compared to earlier designs.
The Kamov Ka-60 was intended to fulfill military requirements such as aerial reconnaissance, troop transport for air-assault forces, radio-electronic jamming, special operations missions, and light transport duties. Internal payload capacity is specified at up to 2,000 kg, and external capacity at up to 2,500 kg. Internally, it is specified to carry 14 infantry troops or 6 stretchers. Variations for foreign sale were anticipated. The Russian Aerospace Forces had an order for 100 units.
Main Variants:
-
Ka-60: The basic multi-role model designed for military tasks.
-
Ka-60U: A training version equipped with dual controls.
-
Ka-60K: A naval version adapted for maritime operations.
-
Ka-60R: A reconnaissance version intended for aerial surveillance.
-
Ka-62: A new version for the civilian market, featuring a redesigned fuselage, larger cabin, and Turbomeca Ardiden 3G engines.
Technical specifications
| Version: Ka-60 | |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 300 km/h (186 mph) |
| Height | 4.6 m (15.1 ft) |
| Length | 15.6 m (51.2 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 5,150 m (16,896 ft) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 6,500 kg (14,330 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 10.4 m/s (34.1 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Rybinsk RD-600V delivering 956 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Russia | 0 (+100) | |
All operators