Juliett-class
Summary
| Origin country | 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR |
| Category | Submarine |
| Subtype | Diesel-electric cruise missile submarine |
| Manufacturer | Baltic Shipyard |
| Year commissioned | 1963 |
| Units | K-156, K-85, K-70, K-24, K-68, K-77, K-81, K-63, K-58, K-73, K-67, K-78, K-203, K-304, K-318, K-120 |
Operators
Technical specifications
| Displacement | 3174 tons |
| Displacement submerged | 3750 tons |
| Range | 18000 km at 7 knots |
| Endurance | 90 |
| Crew | 78 members |
| Width | 9.7 m (31.8 ft) |
| Length | 85.9 m (281.8 ft) |
| Max. depth | 300 m (984.3 ft) |
| Propulsion | 2 × diesel engines (4,000 PS (2,900 kW)), 2 × electric motors (3,000 PS (2,200 kW)), 2 × electric motors (200 PS (150 kW)) |
| Armament | |
| Maximum speed | 16 knots |
| Max. speed submerged | 18 knots |

Description
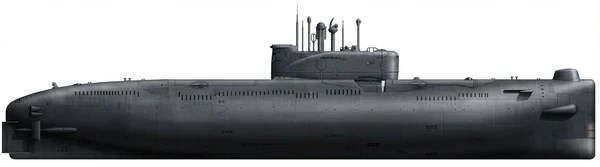
Project 651, designated by NATO as the Juliett class, was a series of Soviet diesel-electric cruise missile submarines designed in the late 1950s. The design team, led by Abram Samuilovich Kassatsier, intended the class to provide a nuclear strike capability against aircraft carrier groups and targets along the United States east coast. The Soviet Navy ordered the Juliett class into production as a conventional alternative to nuclear-powered designs because nuclear reactor production could not meet immediate demand.
The submarines utilize a double-hull design constructed with austenitic steel to maintain a low magnetic signature. The external hull is covered with sound-absorbing hard rubber tiles. The class features missile launchers positioned fore and aft of the sail. Launching missiles required the vessel to surface and maintain a speed of less than four knots. Missile guidance was facilitated by an Argument radar antenna integrated into the forward edge of the sail, which rotated 180 degrees for operation. This was supplemented by a Front Piece datalink and, on certain units, satellite targeting systems. The outer hull contains blast deflectors that increase noise levels at high speeds. The propulsion system relies on diesel engines and electric motors, with a snorkel allowing for diesel operation while submerged. Armament also includes torpedo tubes located in the bow and stern.
The Soviet Union completed 16 of a planned 35 units between 1963 and 1968. Production took place at the Baltic Shipyard in Leningrad and the Krasnoye Sormovo Shipyard in Gorky. The class remained in service through the 1980s, and all units were retired by 1994. Following decommissioning, two vessels were preserved as museum exhibits: K-24 in Germany and K-77 in the United States. K-77 was subsequently scrapped after sinking during a storm in 2007.