Estonian Air Force
Key facts
| Official Name | Estonian Air Force |
| Local Name | Eesti Õhuvägi |
| Country | 🇪🇪 Estonia |
| World rank | #154 |
| Active aircraft | 5 as of 2026 |
| Aircraft on order | 0 |
| Roundel |
|
Global Air Force Index
| 💥 Strategic Bombers | 0 | Nuclear-capable strike aircraft (highest weight) |
| ✈️ Combat Aircraft | 0 | Fighters, multirole & attack aircraft |
| 🚁 Helicopters | 0 | Attack, transport & utility rotorcraft |
| 🛫 Transport | 2 | Strategic & tactical airlift |
| 📊 Total Active | 5 | All aircraft types |
Methodology: Square root scaled index weighted by aircraft combat capability. Strategic bombers score highest due to nuclear strike capability.
Aircraft by type in 2026
| Aircraft type | Active | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
3 | |
|
|
2 | |
Origin countries of aircraft
| Country | Active Aircraft | |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 3 | |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 2 | |
Evolution of Estonian Air Force fleet
Overview
The Estonian Air Force is structured as a surveillance, air defense, and transport force, fully integrated within the NATO command and control structure. Without its own combat aircraft, its primary strategic doctrine is to maintain national airspace integrity through a robust air surveillance system and to facilitate the collective defense of NATO allies through the Baltic Air Policing mission. The force is organized around the Ämari Air Base, which serves as a host installation for rotating NATO fighter detachments and houses the national air surveillance and air defense assets. This structure dictates an operational focus on airspace control, host nation support, and providing airlift and reconnaissance capabilities to the Estonian Defence Forces.
The core of Estonia’s air capability is the Air Surveillance Wing, which operates a network of radars integrated into the NATO Integrated Air and Missile Defence System (NATINAMDS). This system provides persistent airspace monitoring and is the cornerstone of the country's air defense posture. While it relies on allied aircraft for air combat patrols, a significant modernization effort has established a ground-based air defense capability. In 2023, the Air Force activated an Air Defence Wing equipped with the IRIS-T SLM medium-range air defense system. This provides a domestic capability to engage air and missile threats up to 40km in range and 20km in altitude.
Modernization has been focused and pragmatic. The Ämari Air Base was comprehensively renovated, a project completed in 2024 with co-funding from Luxembourg, to solidify its ability to support sustained NATO operations. The acquisition of the IRIS-T SLM system marks a critical evolution from a purely surveillance-oriented force to one with its own defensive strike capacity. For transport and training, the air force uses a small fleet of utility and transport aircraft. The force retired its Robinson R-44 helicopters in December 2024.
Full inventory in 2026
Estonian Air Force
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An-28/M28 | 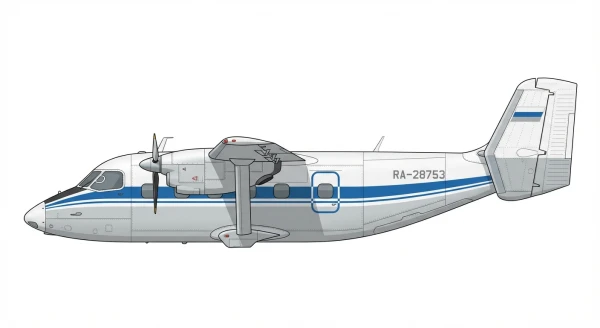 |
🇺🇦 | 1986 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| R44 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1993 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
Frequently Asked Questions
How many aircraft does Estonia have?
How does Estonia's air force rank globally?
What is the Air Force Index of Estonia?
Where does Estonia get its military aircraft from?
Last updated on 27 June 2025. Suggest a change
