Be-12 Tchaïka Mail
Summary
| Category | Military Special Mission Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR |
| Manufacturer | Beriev |
| First flight | 18 October 1960 |
| Year introduced | 1960 |
| Number produced | 150 units |
| Average unit price | $10 million |
Technical specifications
| Version: Be-12P-200 | |
|---|---|
| Operational range | 1,500 km (932 mi) |
| Wingspan | 29.8 m (97.9 ft) |
| Height | 9.1 m (29.9 ft) |
| Length | 26.5 m (87.0 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 8,000 m (26,247 ft) |
| Empty weight | 25,500 kg (56,218 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 36,000 kg (79,366 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 9.5 m/s (31.2 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Ivchenko-Progress AI-20D delivering 3810 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Russia | 7 | |

Description
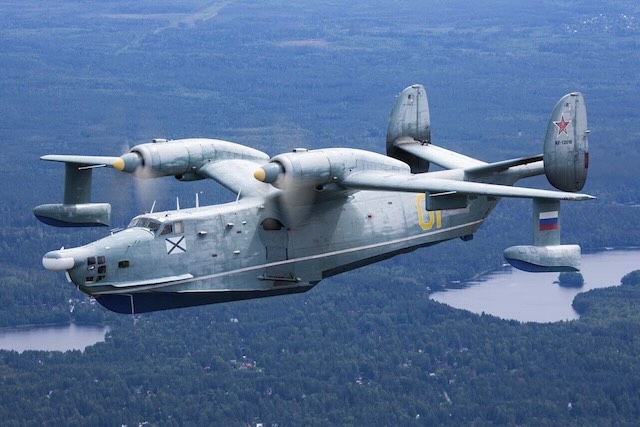
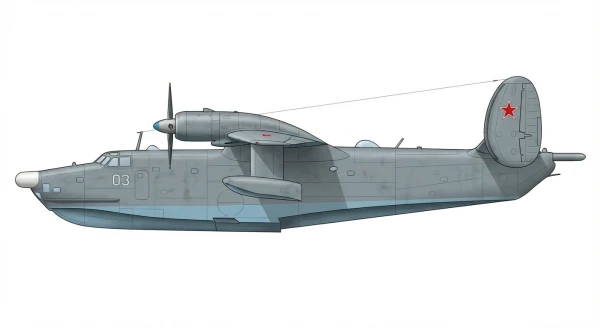
The Beriev Be-12 was developed in the 1950s as a successor to the Beriev Be-6 flying boat. It inherited the gull wing and twin oval tailfin configuration of the Be-6 but incorporated turboprop engines, which provided improved speed and range compared to its predecessor. A significant design enhancement was the addition of retractable landing gear, enabling the aircraft to operate from both land runways and water surfaces. The Be-12's primary roles were anti-submarine warfare and maritime patrol. The first flight occurred on October 18, 1960, at Taganrog airfield, followed by a public debut at the 1961 Soviet Aviation Day at Tushino airfield. Production concluded in 1973, with a total of 150 aircraft constructed across various versions.
The Beriev Be-12 was primarily designed for anti-submarine warfare and maritime patrol. The Be-12SK variant was specifically utilized for testing the SK-1 nuclear depth charge. The Be-12N, an upgraded ASW version, was fitted with the Nartsiss search/attack system.
Entering service with Soviet Naval Aviation in the early 1960s, the Be-12 initially fulfilled maritime patrol and anti-submarine warfare roles. Its deployment positioned it as one of the few amphibious aircraft remaining in military service. A shift in United States Navy submarine capabilities prompted the conversion of some Be-12s into search and rescue platforms (Be-12PS). Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, certain aircraft were adapted as water bombers for combating forest fires. A modified Be-12P, designated "12 Yellow" and later registered as RA-00046 with the designation Be-12P-200, was utilized during the development of the Beriev Be-200 to test fire-fighting equipment and trial operations. The Russian Navy reportedly operated 55 aircraft in 1993, decreasing to 12 by 2005, and nine by 2008. The aircraft have been reported to conduct patrols along the Crimean coast during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. In addition to service in the Soviet Union, Russia, and Ukraine, the Be-12 was also operated by the Egyptian Air Force with Soviet crews for surveillance of the United States Navy's 6th Fleet in the Mediterranean, as well as by the Air Forces of Azerbaijan, Syria, and Vietnam.
Main Variants:
-
Be-12: The primary twin-engine maritime reconnaissance and anti-submarine warfare flying boat, with 2 prototypes and 130 production airframes constructed.
-
Be-12LL: A conversion used for testing the 3M-80 'Moskit' anti-shipping missile, distinguished by a missile seeker head replacing the nose radar, with only one aircraft converted in 1980.
-
Be-12N: An ASW variant enhanced with new sensors, avionics, a Magnetic Anomaly Detector (MAD) sensor, and the Nartsiss search/attack system, involving the conversion of 27 aircraft.
-
Be-12P: A firefighting version equipped with one 4,500 L tank and two 750 L tanks, with four aircraft converted for this role in 1992.
-
Be-12PS: The maritime search and rescue version configured with life rafts and survival equipment, accommodating a crew of six, with ten built new and four converted from the standard Be-12.