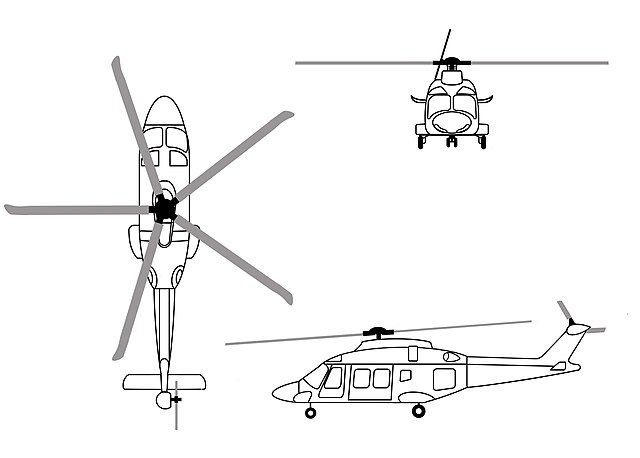
AW169
Summary
| Category | Military Training Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom • 🇮🇹 Italy |
| Manufacturer | AgustaWestland |
| First flight | 10 May 2012 |
| Year introduced | 2015 |
| Number produced | 130 units |
| Average unit price | $9 million |
Description
On 19 July 2010, AgustaWestland announced the development of the AW169 at the Farnborough International Air Show. This 4.5-ton light-intermediate twin-engine rotorcraft was designed for various utility operations with significant commonality in components and cockpit configuration with the AgustaWestland AW139. The British Government provided a $33 million loan for its development program in 2011, followed by a €272 million zero-interest loan approved by the European Union in 2012. The first prototype flew on 10 May 2012. The testing program involved four prototypes. The European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) issued its certification on 15 July 2015, with FAA certification following in February 2016. Production of the AW169 began in Vergiate, Italy, in January 2015, and later commenced briefly in Philadelphia, USA before Leonardo abandoned the planned US production in October 2016.
The AW169 is a medium-sized twin-engine helicopter with a capacity for 7–10 passengers. It is powered by two Pratt & Whitney Canada PW210A FADEC turboshaft engines. These engines enable the main rotor to be driven at variable speeds, reducing external noise and increasing efficiency. The main rotor blades incorporate newly developed dampers to reduce vibration levels. It is the first production helicopter in its category equipped with electronically actuated landing gear. The avionics include a Rockwell Collins glass cockpit featuring three touchscreen displays, digital maps, dual radar altimeters, automatic dependent surveillance – broadcast tracking, Health and usage monitoring systems (HUMS), and night vision goggles (NVG) compatibility. The cockpit and avionics share commonality with the AgustaWestland AW139 and AW189. A four-axis digital automatic flight control system and a dual flight management system, incorporating terrain and traffic avoidance systems, enable single-pilot operation under instrument flight rules (IFR). It does not utilize an auxiliary power unit; instead, a clutch on the transmission allows the rotors to be stopped while the port engine powers avionics and electrical systems. A full or limited ice protection system can be optioned by customers. Optional equipment available includes auxiliary fuel tanks, a rescue hoist, cargo hook, emergency flotation aids, external cameras, rappelling fittings, a wire strike protection system, mission consoles, external loudspeakers, and various external lighting arrangements.
The AW169 has been deployed across a variety of roles since its introduction. A militarized variant, the AW169 AAS, was proposed for the United States Army's Armed Aerial Scout program in April 2013. The launch customer for the type was Lease Corporation International (LCI), with initial units configured for offshore operations. The AW169 entered service with the Kent, Surrey and Sussex Air Ambulance, becoming the first Helicopter Emergency Medical Services (HEMS) operator to utilize the type in the United Kingdom. Air-rescue operator REGA collaborated with AgustaWestland to develop a dedicated search and rescue (SAR) variant. By February 2016, at least 20 AW169s had been delivered globally for EMS, VIP transport, utility, and offshore duties. In July 2017, the National Police Directorate of Norway contracted for three AW169s to replace their Eurocopter EC135s. The Austrian Defense Ministry acquired 18 AW169s in September 2020 to replace their Alouette III helicopters. In July 2023, Ascent Helicopters Ltd. in Canada secured a contract to operate seven new AW169s for British Columbia’s air-ambulance service. In March 2024, North Macedonia finalized a contract for four AW169Ms for fleet modernization.
Main Variants:
-
AW169: The overall designation for the primary type of the helicopter.
-
AW169 AAS: A militarized variant that was proposed for the Armed Aerial Scout program, which was later cancelled.
-
AW169M: A multirole variant designated UH-169A ordered by the Italian Guardia di Finanza for law enforcement and security operations.
-
UH-169D Light Utility Helicopter: A militarized version intended for the Italian Army, configured for troop transport, utility support, armed reconnaissance, and close air support missions.
Technical specifications
| Version: AW169M | |
|---|---|
| Height | 4.5 m (14.8 ft) |
| Length | 14.7 m (48.1 ft) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 4,500 kg (9,921 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Pratt & Whitney Canada PW210A delivering 750 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Austria | 6 (+30) | |

|
Dominican Republic | 2 | |
|
Italy | 2 | |
|
North Macedonia | 0 (+4) | |
All operators