Fuji T-3
Summary
| Category | Military Training Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇯🇵 Japan |
| Manufacturer | Fuji |
| First flight | 26 September 1974 |
| Year introduced | 1978 |
| Number produced | 50 units |
Technical specifications
| Version: T-3 | |
|---|---|
| Operational range | 1,038 km (645 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 377 km/h (234 mph) |
| Wing area | 16.5 m² (177.6 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 10 m (32.8 ft) |
| Height | 3.0 m (9.9 ft) |
| Length | 8.0 m (26.4 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 8,169 m (26,801 ft) |
| Empty weight | 1,120 kg (2,469 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 1,510 kg (3,329 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 7.7 m/s (25.3 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 1 x pistons engine Lycoming IGSO-480-A1A6 delivering 254 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Japan | 81 | |
All operators
Description
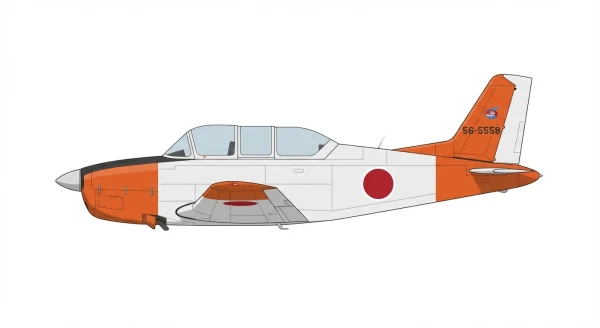
The Fuji T-3's development was initiated to meet the Japan Air Self-Defense Force's (JASDF) need for a primary trainer aircraft. It was derived from the Fuji KM-2, itself a four-seat development of the T-34 Mentor, enhanced with a more powerful engine. The T-3 project combined the structure and engine of the KM-2 with the tandem cockpit design of the T-34 Mentor. The first flight took place on January 17, 1978, marking a key milestone. Fifty aircraft were purchased by the JASDF under the designation Fuji T-3, with production continuing until 1982.
The Fuji T-3 combines the structure and engine of the Fuji KM-2 with the tandem cockpit of the T-34 Mentor. Its wings utilize a NACA 23016.5 airfoil at the root and a NACA 23012 airfoil at the tip. It is powered by a single Lycoming IGSO-480 6-cylinder horizontally opposed air-cooled piston engine, which drives a 3-bladed constant-speed propeller.
As a primary military trainer aircraft, the Fuji T-3 is not equipped with any internal or external armament systems. Its primary function is flight instruction, precluding the need for offensive or defensive weapon systems. The aircraft’s design and operational profile focus on providing a stable and reliable platform for trainee pilots to develop fundamental flying skills. The T-3 lacks hardpoints or internal bays for carrying munitions, rockets, or any other type of armament.
The Fuji T-3 primarily served with the 11 and 12 Hiko-Kyoikudan (flying training wing) of the Japan Air Self-Defense Force, fulfilling its role as a primary trainer aircraft. The T-3 was retired in 2007 and subsequently replaced by the Fuji T-7, which is a turboprop variant of the T-3, upgraded with a 400 shp (300 kW) Allison 250 engine, marking the end of its service in the JASDF.
Main Variants:
-
KM-2B: This was the initial prototype version, developed from the Fuji KM-2.
-
T-3: The primary production variant, procured by the JASDF for basic flight training.