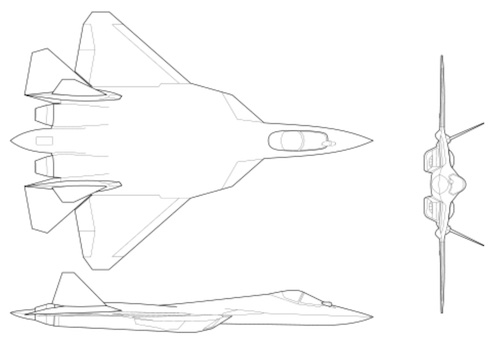
Su-57 Felon
Summary
| Category | Combat Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇷🇺 Russia |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi |
| First flight | 29 January 2010 |
| Year introduced | 2020 |
| Number produced | 32 units |
| Average unit price | $50 million |
Description
The Sukhoi Su-57 is a product of the PAK FA programme, initiated in 1999 to develop a modern and more affordable fifth-generation fighter to succeed the MiG-29 and Su-27. Following a competition, the Russian Ministry of Defence selected Sukhoi as the lead designer in 2002. Development was protracted, marked by technical and structural challenges, including early prototypes exhibiting inadequate fatigue life which necessitated a significant structural redesign. An intended partnership with India to co-develop the FGFA derivative was ultimately dissolved in 2018. The first prototype, designated T-50, achieved its maiden flight on 29 January 2010. After a series of delays, including the crash of the first serial production airframe, the Su-57 officially entered service with the Russian Aerospace Forces in December 2020 under a revised plan to procure 76 aircraft by 2028.
The Su-57 is a twin-engine multirole fighter designed for stealth, supermaneuverability, and supercruise. Its airframe features a blended wing body, widely spaced engines, and all-moving horizontal and vertical stabilizers. Unique aerodynamic features include large leading-edge root extensions fitted with adjustable vortex controllers (LEVCONs) that enhance high angle-of-attack control. The aircraft makes extensive use of composite materials, which comprise approximately 70% of its outer surface. Its design emphasizes frontal stealth, incorporating planform edge alignment, radar-absorbent materials, and internal weapons bays. The engine inlets feature partial serpentine ducts and a blocker grid to obscure the engine face. The avionics are centered on the Sh-121 multifunctional integrated radio electronic system, which includes the N036 Byelka AESA radar, and the 101KS "Atoll" electro-optical system. Production models are powered by two Saturn AL-41F1 engines equipped with canted thrust-vectoring nozzles, enabling maneuverability in all three axes.
For internal carriage, the Su-57 is equipped with two tandem main weapon bays and two smaller side bays. Its armament for air-to-air engagements typically consists of four R-77M medium-range missiles in the main bays and two R-74M2 short-range missiles in the side bays. The aircraft is also capable of carrying the long-range izdeliye 810 missile. For ground attack missions, it can be armed with KAB-250 or KAB-500 precision-guided bombs, Kh-38M air-to-ground missiles, Kh-59MK2 (Kh-69) cruise missiles, and Kh-58UShK anti-radiation missiles. For missions not requiring stealth, the Su-57 can utilize six external hardpoints to carry a wide array of Russian tactical ordnance up to a maximum payload of 7,500 kg. A 30 mm GSh-30-1 autocannon with 150 rounds is mounted internally.
The Su-57 underwent combat evaluation in Syria in February 2018, where prototypes reportedly conducted combat trials, including the launch of a cruise missile. The aircraft has also been deployed during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, primarily used to launch long-range missiles from within the relative safety of Russian airspace. Russian sources have claimed the Su-57 performed successfully in a Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) role, though such claims lack independent verification. The platform's operational readiness has been tested by events such as a fire that severely damaged a prototype in 2014 and the crash of the first serial aircraft in 2019. In June 2024, Ukrainian military intelligence claimed to have damaged at least one Su-57 in a drone strike on Akhtubinsk air base. The aircraft is currently in service only with the Russian Aerospace Forces.
Main Variants
- Su-57: The baseline production version designed for the Russian Aerospace Forces, which began flight testing in 2010 as the T-50 prototype.
- Su-57E: An export variant marketed as the Perspective Multirole Fighter (PMF), featuring system modifications to accommodate foreign customers.
- Su-57M: A planned upgraded version incorporating enhanced mission systems, reliability improvements, and the more powerful Saturn AL-51F-1 engines.
- Sukhoi/HAL FGFA: A proposed derivative for the Indian Air Force with specified improvements, from which India withdrew in 2018 before a prototype was built.
Technical specifications
| Version: Su-57 Felon | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 1 |
| Operational range | 3,500 km (2,175 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 2135 km/h (1327 mph) |
| Wing area | 78.8 m² (848.2 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 14.1 m (46.3 ft) |
| Height | 4.6 m (15.1 ft) |
| Length | 20.1 m (65.9 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 20,000 m (65,617 ft) |
| Empty weight | 18,500 kg (40,785 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 35,000 kg (77,162 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 x Saturn AL-41F1 afterburning turbofan delivering 9000 kgf each |
| Ejection seat | NPP Zvezda K-36D-5 |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Russia | 24 (+52) | |
All operators
Armament