Tunisian Air Force
Key facts
| Official Name | Tunisian Air Force |
| Local Name | القوات الجوية التونسية (Al Quwwāt al Jawwiya at Tūnisiya) |
| Country | 🇹🇳 Tunisia |
| World rank | #67 |
| Active aircraft | 154 as of 2026 |
| Aircraft on order | 21 |
| Roundel |
|
Global Air Force Index
| 💥 Strategic Bombers | 0 | Nuclear-capable strike aircraft (highest weight) |
| ✈️ Combat Aircraft | 13 | Fighters, multirole & attack aircraft |
| 🚁 Helicopters | 101 | Attack, transport & utility rotorcraft |
| 🛫 Transport | 14 | Strategic & tactical airlift |
| 📊 Total Active | 153 | All aircraft types |
Methodology: Square root scaled index weighted by aircraft combat capability. Strategic bombers score highest due to nuclear strike capability.
Aircraft by type in 2026
| Aircraft type | Active | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
101 | |
|
|
25 | |
|
|
15 | |
|
|
13 | |
Origin countries of aircraft
| Country | Active Aircraft | |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 111 | |
| 🇫🇷 France | 21 | |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 17 | |
| 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 5 | |
Evolution of Tunisian Air Force fleet
2 recent updates applied to this inventory
| Date | Aircraft | Active Δ | Ordered Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 Jan 2026 | C-130B/H | +1 | — |
| Fourth C-130H delivered by US at Sidi Ahmed AB; strengthening airlift and rapid response capability. [Source] | |||
| 16 Jun 2025 | Bell 412 | — | +12 |
| At Le Bourget, Bell announced Africa’s first 412EPX order: 12 multi-role helicopters for Tunisia. [Source] | |||
Overview
The Tunisian Air Force is a compact and defensively oriented service structured to address national security threats, primarily terrorism and illicit trafficking. Its personnel and assets are distributed across key air bases, including Bizerte-Sidi Ahmed, Gafsa, Sfax-Thyna, and La Karouba, ensuring operational reach over the country's territory and its strategic Mediterranean borders. The force is organized into several squadrons dedicated to combat, transport, and training roles.
Operational capabilities are centered on border surveillance, intelligence gathering, and support for ground forces. The air force's capacity is not designed for significant power projection but is tailored for counter-terrorism and internal security operations. This is reflected in its helicopter fleet, used for mobility and medical evacuation, and its growing fleet of reconnaissance aircraft. The service also provides critical airlift for the armed forces and contributes to humanitarian relief and firefighting efforts.
The strategic doctrine of the Tunisian Air Force is strictly defensive, shaped by its geographic location and the instability in neighboring Libya. This doctrine emphasizes border security and countering transnational threats, with a notable absence of an offensive posture or expansionist ambitions. A fundamental element of its strategy is close cooperation with international partners, particularly the United States and European nations, which provides access to advanced training, equipment, and intelligence-sharing capabilities. This is further demonstrated through regular participation in joint exercises.
Recent engagements for the air force are primarily within the scope of counter-terrorism operations, although specific details are limited. These activities heavily involve intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions to monitor an active insurgency and secure the border regions. The air force supports ground operations with transport and has deployed personnel to United Nations peacekeeping missions, such as in the Central African Republic, for air rescue and transport duties.
A current initiative is the "2030 Aviation Modernization Plan," heavily supported by the United States. This includes the acquisition of T-6C Texan II trainers to build a new generation of pilots and the purchase of AT-6C Wolverine light attack aircraft. The transport fleet is being bolstered with additional C-130H/J Super Hercules aircraft, while the ISR capabilities have been significantly upgraded through the acquisition of specially configured Cessna 208 Caravan aircraft and UH-60 Black Hawk helicopters.
Full inventory in 2026
Tunisian Air Force
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-5E | 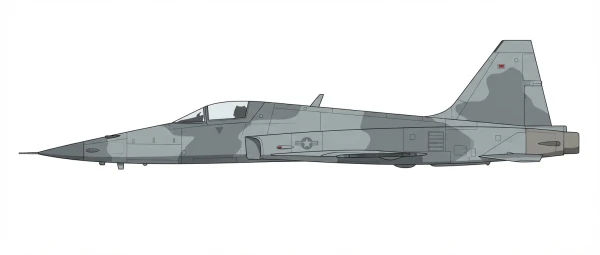 |
🇺🇸 | 1976 | 10 | 0 |
0 |
||
| F-5F |  |
🇺🇸 | 1965 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Bell 205 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1959 | 21 | 0 |
0 |
||
| OH-58 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1967 | 18 | 0 |
0 |
||
| UH-1H/N |  |
🇺🇸 | 1959 | 16 | 0 |
0 |
||
| S-61/CH/HH-3E |  |
🇺🇸 | 1961 | 15 | 0 |
0 |
||
| S-70/UH-60M |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| SE313 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1957 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| SA316 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1961 | 7 | 0 |
0 |
||
| H125M/AS350 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1990 | 6 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Bell 412 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1959 | 2 | 0 |
12 |
||
| L-410 |  |
🇨🇿 | 1970 | 5 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Cessna 208 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1984 | 4 | +4 |
0 |
||
| C-130B/H | 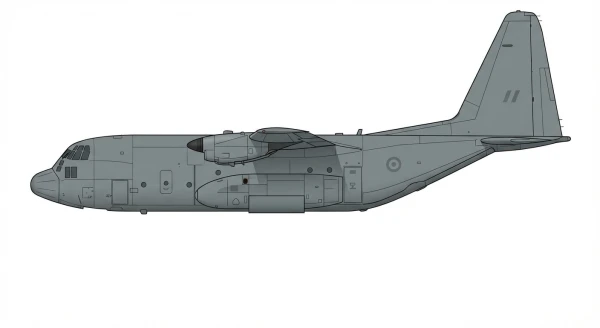 |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 4 | +1 |
1 |
||
| C-130J |  |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| SF-260 |  |
🇮🇹 | 1966 | 17 | 0 |
0 |
||
| T-6C |  |
🇺🇸 | 2001 | 8 | 0 |
4 |
||
| AT-6C |  |
🇺🇸 | 2001 | 0 | 0 |
4 |
Frequently Asked Questions
How many aircraft does Tunisia have?
How does Tunisia's air force rank globally?
How many combat aircraft does Tunisia operate?
How many military helicopters does Tunisia have?
What is the Air Force Index of Tunisia?
Where does Tunisia get its military aircraft from?
Last updated on 13 January 2026. Suggest a change
