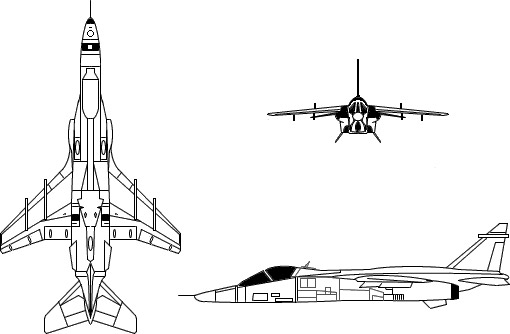
Jaguar
Summary
| Category | Combat Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇫🇷 France • 🇬🇧 United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | SEPECAT |
| First flight | 8 September 1968 |
| Year introduced | 1972 |
| Number produced | 573 units |
| Average unit price | $10 million |
Description
The Jaguar program originated in the early 1960s from British Air Staff Target 362, specifying an advanced supersonic jet trainer, and the French École de Combat et d'Appui Tactique (ECAT), requiring a dual-role subsonic trainer and light attack aircraft. In 1966, SEPECAT, a joint venture between Breguet and the British Aircraft Corporation, was established for airframe production. The design, while partly based on the Breguet Br.121, incorporated significant BAC design elements, particularly the wing and high-lift devices. Concurrently, a partnership between Rolls-Royce and Turbomeca developed the Adour afterburning turbofan engine. The first of eight prototypes, a two-seat aircraft fitted with the initial production Adour engine, conducted its maiden flight on 8 September 1968, achieving supersonic speed on its third flight.
The Jaguar is a single-seat, swept-wing, twin-engine monoplane configuration, equipped with tall tricycle-type retractable landing gear. In its original iteration, it possessed a maximum take-off weight in the 15-tonne class. It featured hardpoints capable of carrying an external weapons load up to 10,000 lb (4,500 kg).
The aircraft had hardpoints for an external weapons load of up to 10,000 lb (4,500 kg). Typical ordnance included Matra LR.F2 rocket pods, BAP 100-mm bombs, Martel AS.37 anti-radar missiles, AIM-9 Sidewinder missiles, and Rockeye cluster bombs. During the Gulf War, RAF Jaguars were adapted to carry CRV7 high-velocity rockets and American CBU-87 cluster bombs. The Jaguar was armed with a pair of 30 mm autocannons, either the French DEFA cannon or the British ADEN cannon. A feature available on the Jaguar International and later adopted by RAF Jaguars in the buildup to Operation Granby in 1990 was the option of overwing pylons for short-range air-to-air missiles like the Matra R550 Magic or Sidewinder, which freed up under-wing pylons for other stores. French Jaguars were not modified with overwing pylons. Some Indian Air Force aircraft were equipped with the Agave radar system for maritime strike roles and could carry anti-ship missiles, while other Indian aircraft are configured for delivering nuclear bombs.
The Jaguar was deployed in conflicts in Mauritania, Chad, Iraq, Bosnia, and Pakistan. It served as a nuclear delivery platform for the United Kingdom, France, and India. Its reliability was noted during the Gulf War. The French Air Force operated the Jaguar as its primary strike/attack aircraft until 1 July 2005. The Royal Air Force continued its service until the end of April 2007. The aircraft was eventually replaced by the Dassault Rafale in the French Air Force and the Eurofighter Typhoon in the Royal Air Force.
Main Variants:
-
Jaguar A: Single-seat all-weather tactical strike, ground-attack fighter version for the French Air Force, with 160 production aircraft built.
-
Jaguar B/Jaguar T2: Two-seat training version for the Royal Air Force, also capable of secondary strike and ground attack roles.
-
Jaguar GR1: Single-seat all-weather tactical strike and ground-attack fighter version for the Royal Air Force featuring a NAVigation And Weapon Aiming Sub-System (NAVWASS).
-
Jaguar M: Single prototype of a single-seat naval strike aircraft intended for the French Navy.
-
Jaguar International: Export versions based on either the Jaguar S or Jaguar B, tailored for international customers.
Technical specifications
| Version: Jaguar Marine | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 1 pilot |
| Operational range | 915 km (569 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 1593 km/h (990 mph) |
| Wing area | 24 m² (258.3 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 8.7 m (28.5 ft) |
| Height | 4.9 m (16.1 ft) |
| Length | 15.5 m (50.9 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 14,000 m (45,932 ft) |
| Empty weight | 7,000 kg (15,432 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 15,700 kg (34,613 lbs) |
| Takeoff distance | 565 m (1,854 ft) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turbojets Rolls-Royce-Turbomeca Adour 804 delivering 3000 kgf each |
| Ejection seat | Martin-Baker Mk 9 |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
India | 160 | |
Armament
Missiles payload:
- Air-to-Surface AM39 Exocet
- Air-to-Surface AS.30
- Air-to-Surface AS.37 Martel
- Air-to-Air Short-Range R550 Magic
Bombs payload:
- Anti-Runway Matra BLU-107/B Durandal
- Low-Drag Mk 82
- Anti-Runway Thomson-CSF BAP-100
- Low-Drag Thomson-CSF BAT-120