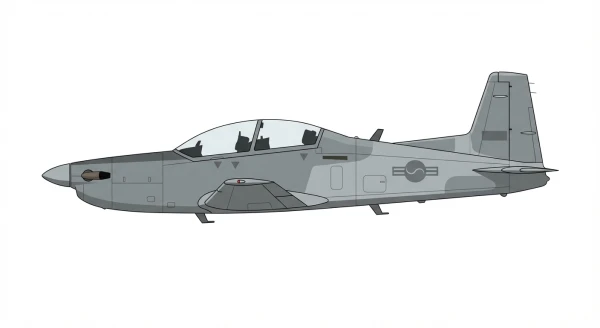
KT-1 Woongbi
Summary
| Category | Military Training Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇰🇷 South Korea |
| Manufacturer | KAI |
| First flight | 12 December 1991 |
| Year introduced | 2000 |
| Number produced | 178 units |
| Average unit price | $9 million |
Technical specifications
| Version: KT-1 | |
|---|---|
| Operational range | 1,333 km (828 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 574 km/h (357 mph) |
| Wing area | 16.0 m² (172.3 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 10.6 m (34.7 ft) |
| Height | 3.7 m (12.1 ft) |
| Length | 10.3 m (33.7 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 11,582 m (37,999 ft) |
| Empty weight | 1,910 kg (4,211 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 2,540 kg (5,600 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 16.2 m/s (53.1 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 1 x pistons engine Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-62 delivering 708 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
South Korea | 103 | |

|
Turkey | 39 (+15) | |

|
Peru | 20 | |
|
Indonesia | 15 | |

|
Senegal | 4 | |
All operators
Description
The KT-1 Woongbi's development originated from the KTX programme, launched in 1988 by the Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF) to produce an indigenous trainer aircraft. This initiative was a collaborative effort between Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI), responsible for detailed design and manufacturing, and the Agency for Defence Development (ADD), which oversaw the project. A series of nine prototypes were constructed, with the first completed in June 1991. The aircraft was officially named 'Woongbi' in 1995, and the final test flight was performed in 1998.
The KT-1 can be configured with either an analog or 'glass' cockpit. Certain variants boast enhanced avionics and systems, including a night vision goggles (NVG)-compatible cockpit, head-up display (HUD), multi-function displays (MFD), GPS/inertial navigation system, mission computer, onboard oxygen generation system, a vapor-cycle environmental control system, and hands-on-throttle-and-stick (HOTAS)-compatible controls. Avionics are sourced from foreign companies like Elbit, Flight Vision, and Thales.
The KT-1 is equipped with the capability to carry various types of guns, bombs, rockets, and missiles, with specific configurations dependent upon customer requirements. It features provision for practice bomb carriers on four underwing pylons. Additional equipment options include external fuel tanks, a centrally mounted forward-looking infrared (FLIR) sensor, and a laser range finder.
The Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF) stands as the primary operator of the KT-1, receiving its first aircraft in 2000. By the end of that year, eight aircraft had been delivered. A follow-on order for 20 aircraft was received in November 2003, ensuring continued production. A significant portion of the ROKAF's KT-1 fleet is equipped with gun pods and rockets for weapons training purposes. One of the first export customers for the KT-1 was Indonesia. As part of an exchange agreement in early 2001, Indonesia bartered 8 CASA/IPTN CN-235 transport aircraft for 12 KT-1 trainers. The Indonesian Air Force also employs the KT-1 with its Jupiter Aerobatic Team. Turkey also acquired 40 (+15) KT-1s, designated KT-1T, through a contract negotiated in June 2007, with the last aircraft delivered in late 2012. In November 2012, a contract was signed with the Peruvian Air Force for 20 KT-1Ps.
Main Variants:
-
KT-1: The basic trainer variant of the ROKAF, it is bigger and heavier than the KTX-1 prototype, featuring relocated tail surfaces and a more powerful Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-62 engine.
-
KA-1: An armed advanced trainer, it boasts light-attack and forward air control capabilities, equipped with a head-up display, MFD panels, and four hardpoints for rocket launchers and gun pods.
-
KT-1B: This is an export version tailored for Indonesia, with some avionics either excluded or replaced with commercial off-the-shelf alternatives to meet specific requirements.
-
KT-1C: An improved, armed export variant featuring a centerline forward-looking infrared pod, it can also be equipped with a 12.7 mm gun pod, chaffs, flares, training missiles, rockets, or unguided bombs.
-
KT-1T: This is the export version specifically designed for Turkey.