An-72/74 Coaler
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR |
| Manufacturer | Antonov |
| First flight | 22 December 1977 |
| Year introduced | 1985 |
| Number produced | 195 units |
| Average unit price | $25 million |
Description
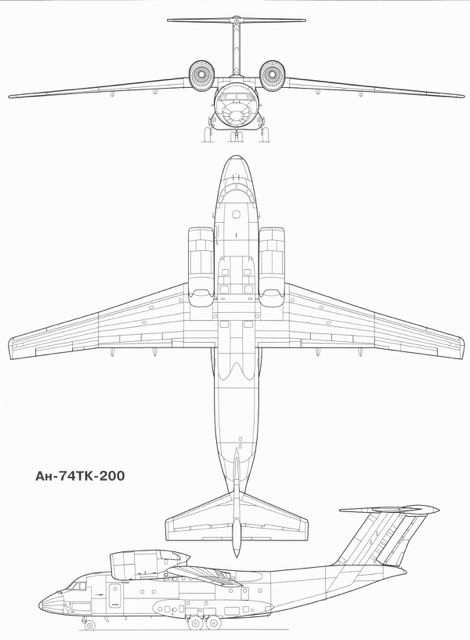
The Antonov An-74's development was initiated as an upgrade to the An-72 test aircraft, with a specific focus on Arctic and Antarctic operations, initially designated An-72A "Arctic". The primary goal was to provide reliable transport for cargo, equipment, and personnel across short- to medium-range routes under extreme climatic conditions, ranging from −60 to 45 °C, at any latitude, including the North Pole, and at high altitudes. It was designed to operate from low-grade airstrips constructed of concrete, pebble, ice, and snow. Produced in conjunction with the An-72, the An-74 was engineered to be equipped with wheel-ski landing gear, de-icing systems, and other enhancements to support operations in Arctic and Antarctic environments. The first flight of the An-74 took place on September 29, 1983, four years after its predecessor, the An-72.
A notable design feature of the An-74 is its utilization of the Coandă effect to achieve improved STOL (Short Takeoff and Landing) performance through engine exhaust gases blown over the wing's upper surface, significantly boosting lift. Power is provided by two Lotarev D-36 turbofan engines. Furthermore, the rear fuselage incorporates a hinged loading ramp complemented by a rear fairing that slides backwards and upwards to clear the opening. The aircraft can be equipped with wheel-ski landing gear and de-icing systems to enable operations in Arctic or Antarctic environments. The avionics bay has been enlarged and radar has been upgraded since the previous An-72 model.
The An-74, while primarily a transport aircraft, possesses variants adapted for military roles. The An-74MP, a marine patrol version, has the capacity to transport 44 soldiers, 22 paratroops, or 16 stretchers with medical staff. The An-74T freighter version is equipped with an internal winch, roller equipment, and cargo mooring points, and can be fitted with static lines for paratroops or dropping air cargo. The general cargo payload is around 11 tons.
The An-74 began its operational career shortly after its first flight in 1983, with cold-weather testing and Arctic operations taking precedence. One notable mission saw an An-74 evacuating the crew of Arctic station SP-32 in March 2004. As of early 2006, a significant number of those registered in Russia were actively in use. Several nations operate military variants, including Egypt with its An-74T-200A aircraft, and Iran, whose An-74TK-200 and An-74T-200 models were later transferred to the Iranian Revolutionary Guard. However, the aircraft has also experienced a number of accidents and incidents, including fatal crashes in Russia, Cameroon, and Iran, as well as write-offs and damage sustained during operations in Mali and São Tomé, and during the battle of Hostomel in Ukraine in 2022.
Main Variants:
-
An-74: This is the Arctic/Antarctic support model, designed with a five-person crew capacity and enhanced with increased fuel capacity and improved navigation and de-icing systems.
-
An-74-200: A military transport variant that builds upon the An-74T freighter model.
-
An-74-200D: This VIP/executive transport version is based on the An-74TK-200 convertible model, offering luxury and comfort for its passengers.
-
An-74A: A versatile model designed to function either as a passenger carrier or a freighter, adapting to various operational needs.
-
An-74MP: Designated for maritime patrol, this version has the capacity to transport 44 soldiers, 22 paratroopers, 16 stretchers with medical staff, or ten tonnes of cargo.
Technical specifications
| Version: An-74 | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 5 members |
| Operational range | 4,800 km (2,983 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 700 km/h (435 mph) |
| Wing area | 98.6 m² (1061.5 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 31.9 m (104.6 ft) |
| Height | 8.7 m (28.4 ft) |
| Length | 28.1 m (92.1 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 11,600 m (38,058 ft) |
| Empty weight | 19,000 kg (41,888 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 34,800 kg (76,721 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 × turbofans Ivchenko-Progress D-36 delivering 8385 kW |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Russia | 35 | |

|
Iran | 14 | |

|
Angola | 4 | |

|
Egypt | 3 | |

|
Turkmenistan | 2 | |
| 🇨🇩 | Congo Democratic Republic | 1 | |

|
Kazakhstan | 1 | |
|
Libya | 1 | |
All operators