Ka-27 Helix
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopter |
| Origin country | 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR |
| Manufacturer | Kamov |
| First flight | 8 August 1973 |
| Year introduced | 1982 |
| Number produced | 201 units |
Description
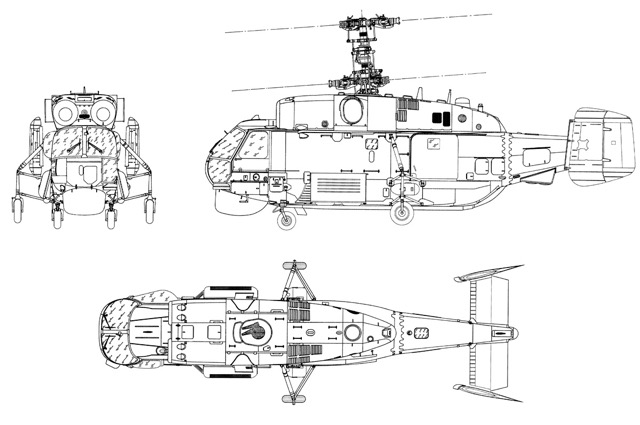
The Kamov Ka-27 was specifically developed for the Soviet Navy to fulfill roles in ferrying and anti-submarine warfare, intended to replace the Kamov Ka-25. Design work commenced in 1969, with a critical requirement that the new helicopter’s external dimensions be no larger than its predecessor. A key design feature, common among Kamov military helicopters, is the adoption of coaxial rotors to eliminate the need for a tail rotor. The first prototype took flight in 1973, leading to the construction of five prototypes and pre-series helicopters. Series production began in Kumertau in July 1979, and the Ka-27 officially entered service with the Soviet Navy in April 1981.
The Kamov Ka-27 features a coaxial rotor system, a characteristic of Kamov military helicopters, which eliminates the need for a tail rotor. It is constructed with a four-leg fixed landing gear and equipped with two lateral buoys for emergency water landings.
The Ka-27PL anti-submarine warfare variant incorporates a radar system and either a dipping sonar or a magnetic anomaly detector. For engaging underwater targets, it can deploy up to 36 sonobuoys, a single torpedo, or between six and eight conventional depth charges, with the option of a single nuclear depth charge. Specific compatible torpedoes include AT-1M, VTT-1, UMGT-1 Orlan, and APR-2 Yastreb, and compatible sonobuoys include 36 RGB-NM and RGB-NM-1. The Ka-27PS search and rescue version is adapted with accommodations for 12 folding seats or four stretchers, complemented by a 300 kg winch, a rescue hoist, and hooks for external loads; its ASW equipment is removed. The Ka-27PS fuel capacity is 3,450 liters compared to the Ka-27PL's 2,940 liters. The Ka-29TB assault transport is fitted with four external hardpoints for rockets, guns, bombs, munitions dispensers, or special four-round missile launchers for the 9K114 Shturm anti-tank missile. It also features a mobile, forward-firing GShG-7.62 machine gun with 1800 rounds, and optionally, a flexible semi-rigid mounted 30 mm 2A42 cannon with 250 rounds, with ammunition carried in the cabin. The Ka-32A7 variant can carry 2 x GSh-23L 23mm cannons, B-8V-20 rocket pods, or 2 x Kh-35 anti-ship missiles or Kh-25 air-to-air missiles. The Ka-27M represents a modern upgrade, integrating an active electronically scanned array radar, acoustic sensors, magnetometric sensors, and signals intelligence systems, all displayed on onboard instrumentation for comprehensive tactical command.
The Ka-27 has seen deployment in various theaters and has been operated by several air forces globally. A Russian Navy Ka-27 conducted interoperability deck landing training aboard the US command ship USS Mount Whitney in 2010. China has purchased the Ka-28 export version and the Ka-31 radar warning version for its PLAN fleet since the 1990s; revelations of Ka-31 acquisitions surfaced around 2010. It is believed that the Chinese Ka-28s feature enhanced avionics compared to those exported elsewhere. The Ka-27 has also seen use in the Syrian Civil War by the Syrian Navy. A Ka-29 was reportedly shot down over Crimea in June 2024 by a Russian Pantsir-S1 during a Ukrainian drone attack, resulting in the loss of its crew.
Main Variants:
-
Ka-29TB (Helix-B): An assault transport armored helicopter designed to operate from amphibious landing ships or aircraft carriers, accommodating two pilots and 16 troops, and equipped with four hardpoints for various armaments.
-
Ka-28 (Helix-A): An export version of the Ka-27PL, featuring an increased maximum takeoff weight, maximum fuel capacity, and range.
-
Ka-27M: The latest modernized variant, equipped with an advanced radar and tactical command system including acoustic sensors, magnetometric sensors, signals intelligence, and an FH-A radar with an active phased array antenna.
-
Ka-27PL (Helix-A): An anti-submarine warfare helicopter equipped with radar and either a dipping sonar or a magnetic anomaly detector, capable of carrying sonobuoys, torpedoes, conventional depth charges, or a single nuclear depth charge.
-
Ka-27PS (Helix-D): A search and rescue helicopter variant with ASW equipment removed and a winch fitted, capable of carrying 12 folding seats or four stretchers, and equipped with a rescue hoist and hooks for external loads.
Technical specifications
| Version: Ka-27PL Helix-A | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 3 members |
| Maximum speed | 270 km/h (168 mph) |
| Height | 5.5 m (18.0 ft) |
| Length | 11.3 m (37.1 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 5,000 m (16,404 ft) |
| Empty weight | 6,500 kg (14,330 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 12,000 kg (26,455 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 × turbines Klimov TV3-117V delivering 1659 kW |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Russia | 111 | |
|
India | 28 | |

|
China | 27 | |

|
Vietnam | 10 | |

|
South Korea | 7 | |

|
Azerbaijan | 4 | |
|
Ukraine | 4 | |

|
Algeria | 3 | |
| 🇱🇦 | Laos | 2 | |
|
Syria | 2 | |
| 🇬🇶 | Equatorial Guinea | 1 | |
All operators
Armament
Bombs payload:
- Anti-Submarine PLAB-250-120