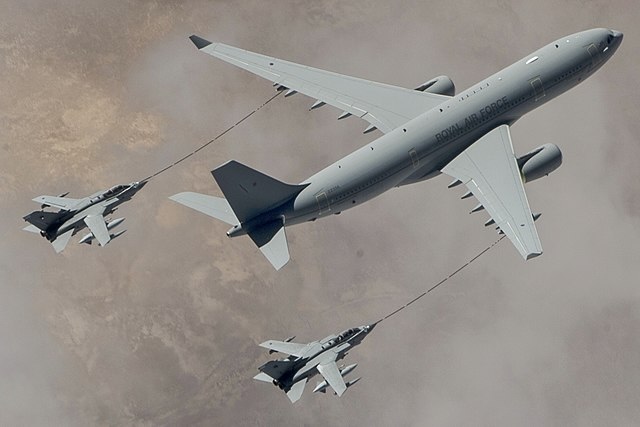
A330
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇪🇺 Europe |
| Manufacturer | Airbus |
| First flight | 2 November 1992 |
| Year introduced | 1994 |
| Number produced | 1577 units |
| Average unit price | $260 million |
Description
Airbus began developing larger A300 derivatives in the mid–1970s, giving rise to the A330 twinjet. The A300B9, a lengthened A300 with the same wing coupled with the most powerful turbofan engines available, targeted demand for high-capacity, medium-range, transcontinental trunk routes and was seen as a replacement for trijets such as the DC-10 and the Lockheed L-1011 TriStar. The A330 shares many underpinnings with the airframe of early A340 variants, notably the same wing components, structure, fly-by-wire controls, and glass cockpit, but has two main landing gear legs instead of three, lower weights, and slightly different fuselage lengths. Airbus launched the design along with first orders in June 1987. The A330-300, the first variant, took its maiden flight in November 1992 and entered service with Air Inter in January 1994. The A330 was Airbus's first airliner to offer a choice of three engines: the General Electric CF6, Pratt & Whitney PW4000, or the Rolls-Royce Trent 700. In July 2014, Airbus announced the re-engined A330neo (new engine option) comprising A330-800 and -900, which entered service with TAP Air Portugal in December 2018.
The airframe features a low-wing cantilever monoplane design, with a wing virtually identical to that of the A340-200/300. Designed and manufactured by BAe, the wings are long and slender, with a high aspect ratio and are swept back at 30 degrees, allowing for a maximum operating Mach number of 0.86. Each wing incorporates a 2.74 m (9 ft 0 in) tall winglet. The fuselage, based on the Airbus A300-600, shares common parts and maintains the same external width of 5.64 m (19 ft) and cabin width of 5.26 m (17 ft). Composite materials constitute 10% of the structure's weight, used for the fin, rudder, elevators, horizontal tail plane (used as fuel tank), flaps, ailerons, and spoilers. While primarily a passenger aircraft, the A330 MRTT military variant is designed for aerial refueling and strategic transport, focusing on transporting cargo and personnel and providing aerial refueling capabilities.
Airbus intended the A330 to compete in the Extended-range Twin-engine Operation Performance Standards (ETOPS) market, specifically with aircraft like the Boeing 767. Instead of an "ETOPS out of the box" approach, ETOPS approval on the A330 was gradually increased using in-service experience. In November 2009, the A330 became the first aircraft to receive ETOPS–240 approval, which has since been offered by Airbus as an option. As of September 2024, the global A330 fleet of 1,471 aircraft had an average age of 12 years (≈2.5 years for A330neo), facilitated the opening of over 350 new city pairs since 2011, accumulated over 65 million flight hours since its entry into service, and maintained a 99.2% operational reliability.
Main Variants:
-
A330-200: A shortened, longer-range variant.
-
A330-200F: An all-cargo derivative of the A330-200.
-
A330-300: Based on a stretched A300 fuselage with new wings, stabilizers and fly-by-wire systems.
-
A330-800: Based on the A330-200, featuring cabin modifications, larger Trent 7000 engines, and aerodynamic improvements.
-
A330-900: Maintains the A330-300 fuselage dimensions but includes cabin optimization, Trent 7000 engines, and redesigned winglets.
Technical specifications
| Version: A330-200 | |
|---|---|
| Wing area | 362 m² (3896.5 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 60.3 m (197.8 ft) |
| Height | 17.4 m (57.1 ft) |
| Length | 59 m (193.6 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 13,000 m (42,651 ft) |
| Empty weight | 119,600 kg (263,673 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 242,000 kg (533,518 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turbojets General Electric CF6-80E1A4 delivering 32659 kgf each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
France | 13 | |
|
United Kingdom | 9 | |

|
Saudi Arabia | 6 (+4) | |

|
Australia | 6 | |

|
Singapore | 6 | |

|
United Arab Emirates | 4 (+1) | |

|
South Korea | 4 | |

|
Brazil | 2 | |

|
Spain | 2 | |

|
Canada | 1 (+8) | |
All operators

