Libyan Air Force
Key facts
| Official Name | Libyan Air Force |
| Local Name | القوات الجوية الليبية (Al Quwwāt al Jawwiyah al Lībiyah) |
| Country | 🇱🇾 Libya |
| World rank | #71 |
| Active aircraft | 141 as of 2026 |
| Aircraft on order | 0 |
| Roundel |
|
Global Air Force Index
| 💥 Strategic Bombers | 0 | Nuclear-capable strike aircraft (highest weight) |
| ✈️ Combat Aircraft | 23 | Fighters, multirole & attack aircraft |
| 🚁 Helicopters | 33 | Attack, transport & utility rotorcraft |
| 🛫 Transport | 14 | Strategic & tactical airlift |
| 📊 Total Active | 141 | All aircraft types |
Methodology: Square root scaled index weighted by aircraft combat capability. Strategic bombers score highest due to nuclear strike capability.
Aircraft by type in 2026
| Aircraft type | Active | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
71 | |
|
|
33 | |
|
|
23 | |
|
|
14 | |
Origin countries of aircraft
| Country | Active Aircraft | |
|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR | 52 | |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 38 | |
| 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 22 | |
| 🇳🇱 Ex-Yugoslavia | 12 | |
| 🇫🇷 France | 8 | |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 5 | |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 4 | |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 3 | |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 1 | |
Evolution of Libyan Air Force fleet
1 recent update applied to this inventory
| Date | Aircraft | Active Δ | Ordered Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23 Dec 2025 | Falcon 50 | -1 | — |
| VIP transport carrying Libyan Chief of Staff crashed near Ankara Turkey due to technical failure. [Source] | |||
Overview
The Libyan Air Force, once a significant regional air arm, has been defined by fragmentation since 2011. The post-Gaddafi era has seen the force effectively split into two main opposing entities, each aligned with the major political factions in the country: the Government of National Unity (GNU) based in Tripoli, and the Libyan National Army (LNA) under the command of Khalifa Haftar, based in the east. This division has resulted in two distinct and rival air arms, with no unified national strategic doctrine.
The structure of both air forces is largely inherited from the pre-2011 inventory, but significantly degraded in terms of operational aircraft and infrastructure. Both factions operate a mix of Soviet-era and French combat aircraft, though the exact number of airworthy platforms remains low and difficult to ascertain precisely. The main operational bases are also divided, with the GNU-aligned forces primarily operating out of bases in the west, such as Misrata, and the LNA controlling key facilities in the east, like Benina Air Base. The command and control for each entity is decentralized and tied to their respective ground force leadership, lacking the sophisticated, integrated structure of a modern air force.
Operational capabilities are severely constrained for both sides. The air arms have been primarily utilized in a ground-attack role in support of their respective land forces during the Second Libyan Civil War. Engagements have largely consisted of air strikes against military and sometimes civilian targets, as well as reconnaissance missions. The use of armed drones, particularly by the LNA and its foreign backers, has also been a significant feature of recent conflicts. The technical expertise and logistical support chains for maintaining the aging fleets are weak, heavily relying on foreign assistance.
There are no comprehensive, national modernization programs in place due to the ongoing political instability and the arms embargo. Any acquisitions or upgrades have been piecemeal, often supplied by international patrons of the respective factions. For the LNA, this has included the alleged supply of refurbished aircraft. For the GNU-aligned forces, foreign support has also been a key factor in sustaining their limited air capabilities. The result is a patchwork of aging and, in some cases, externally-provided air assets, rather than a coherent, modern force.
Full inventory in 2026
Libya Dawn
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiG-25 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1970 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C-130H | 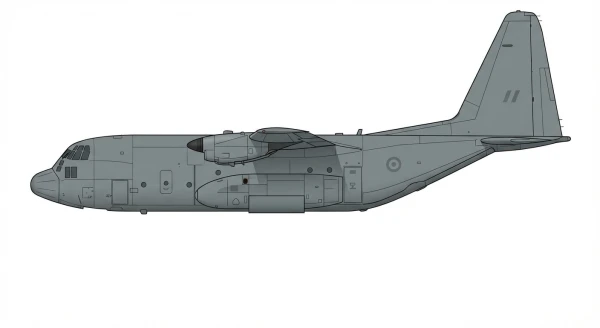 |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
Libyan Air Force
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiG-21 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1958 | 12 | 0 |
0 |
||
| MiG-23 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1970 | 4 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mirage F1 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1973 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Su-24 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1973 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Su-22 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1971 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mi-2 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1965 | 7 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mi-24/35 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1972 | 7 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mi-8/171 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1967 | 6 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mi-14 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1975 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| CH-47C |  |
🇺🇸 | 1962 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AW139 |  |
🇬🇧 🇮🇹 | 2003 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| An-72 | 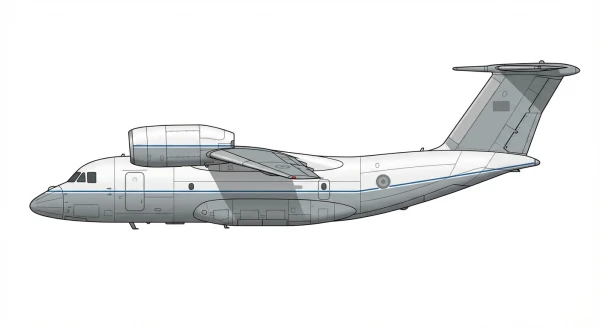 |
🇨🇳 | 1985 | 1 | -1 |
0 |
||
| C-130H |  |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Il-76 | 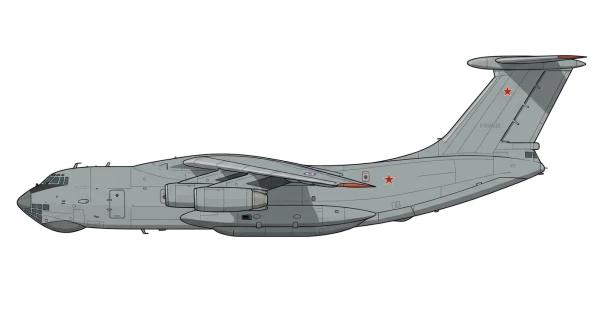 |
🇨🇳 | 1974 | 1 | +1 |
0 |
||
| Falcon 50 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1979 | 0 | 0 |
0 |
||
| SF-260 |  |
🇮🇹 | 1966 | 37 | 0 |
0 |
||
| L-39 |  |
🇨🇿 | 1972 | 21 | +9 |
0 |
||
| G-2 |  |
🇳🇱 | 1965 | 12 | -2 |
0 |
Libyan National Army
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H215/AS332 |  |
🇩🇪 🇫🇷 | 1978 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| SA341 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1971 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mi-8 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1967 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| An-12 |  |
🇺🇦 | 1959 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Il-76 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1974 | 3 | +2 |
0 |
||
| An-32 |  |
🇺🇦 | 1982 | 2 | +1 |
0 |
||
| Il-18 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1957 | 2 | +1 |
0 |
||
| L-39 |  |
🇨🇿 | 1972 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
Frequently Asked Questions
How many aircraft does Libya have?
How does Libya's air force rank globally?
How many combat aircraft does Libya operate?
How many military helicopters does Libya have?
What is the Air Force Index of Libya?
Where does Libya get its military aircraft from?
Last updated on 23 December 2025. Suggest a change