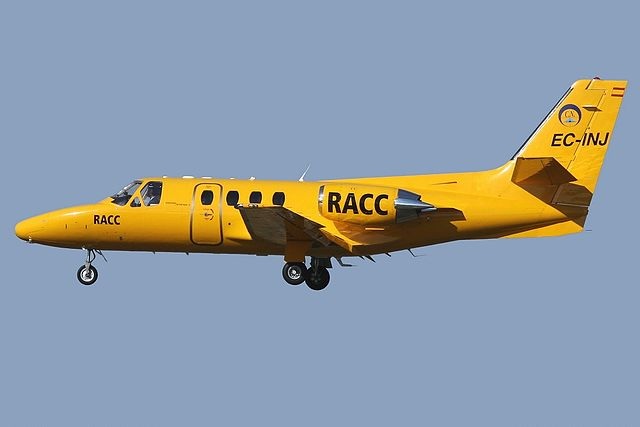
Cessna 500 Citation I
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircrafts |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Cessna |
| First flight | 15 September 1969 |
| Year introduced | 1971 |
| Number produced | 689 units |
| Average unit price | $0.5 million |
Description
In the early 1960s, Cessna identified a market gap between turboprop aircraft and existing light jets, envisioning a jet that was easier to fly, less expensive to maintain, and capable of accessing smaller airports. This led to the announcement of the Fanjet 500 prototype in October 1968, which first flew on September 15, 1969. Originally mocked as the "Nearjet" due to its slower cruise speed compared to other business jets with swept wings and turbojet engines, the aircraft was later renamed the "Citation." After a redesign involving a longer forward fuselage, repositioned engine nacelles, a larger tail, and increased horizontal tail dihedral, it was certified as the 500 Citation on September 9, 1971. The Cessna 500 Citation I is notable for its straight wing design and is powered by two Pratt & Whitney Canada JT15D turbofan engines, a choice influenced by Cessna's prior experience with the T-37 Tweet twinjet trainer. In 1974, thrust reversers became optional, and in 1976, the gross weight was increased. Also in 1976, the wingspan was increased from 43.9 to 47.1 ft (13.4 to 14.4 m). The enhanced 500 Citation I was introduced later in 1976 with the higher gross weight, improved JT15D-1A engines, and the increased span wing. The 501 Citation I/SP, certified for single-pilot operations, was introduced in 1977. Production ceased in 1985 due to JT15D engine price increases, making the Citation II series a more attractive option for buyers. The aircraft were then further developed into the Citation II/Bravo and the Citation V/Ultra/Encore.
The Cessna Citation series has seen operational use across various sectors, including government and military roles. Notably, the National Air Force of Angola, the Argentine Army and Federal Police, the People's Liberation Army Air Force of China, and the air forces of the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Mexico, and Venezuela have incorporated the Citation into their fleets for transport purposes. The operational history is also marked by accidents and incidents. For example, the crash of a Citation I/SP in 1979 resulted in fatalities, attributed to pilot error. Similarly, accidents in 2008 and 2016 involving Citation I/SPs led to multiple fatalities, with causes ranging from improper emergency procedures to spatial disorientation. Another accident occurred in 2021, when a Citation 501 crashed, resulting in fatalities, caused by pilot error related to somatogravic illusion.
Main Variants:
-
500 Citation: The original model, certified in 1971, laid the foundation for the Citation family with its straightforward design and operational ease.
-
Citation I: An upgraded version introduced in 1976, featuring a higher gross weight, improved JT15D-1A engines, and an increased wingspan for enhanced performance.
-
501 Citation I/SP: A variant of the Citation I, this model was certified for single-pilot operations, offering increased flexibility for owner-operators.
Technical specifications
| Version: 500 Citation I | |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 665 km/h (413 mph) |
| Wing area | 25.9 m² (278.5 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 14.4 m (47.1 ft) |
| Height | 4.4 m (14.3 ft) |
| Length | 13.3 m (43.6 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 12,497 m (41,001 ft) |
| Empty weight | 3,008 kg (6,631 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 5,375 kg (11,850 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 13.8 m/s (45.3 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turbofans Pratt & Whitney Canada JT15D-1B delivering 998 kgf each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 38 (+2) | |

|
Spain | 6 | |

|
Colombia | 5 | |

|
Chile | 4 | |

|
Saudi Arabia | 4 | |

|
Mexico | 2 | |

|
Nigeria | 2 | |

|
Angola | 1 | |

|
Argentina | 1 | |

|
Ecuador | 1 | |
|
Pakistan | 1 | |

|
Peru | 1 | |

|
Venezuela | 1 | |
All operators
