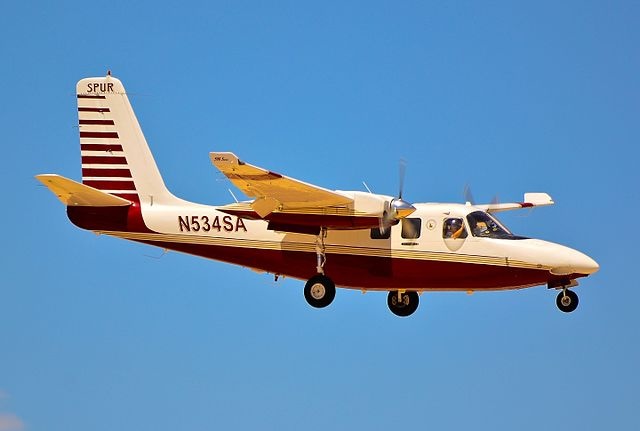
Commander 500
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Aero |
| First flight | 23 April 1948 |
| Year introduced | 1952 |
| Number produced | 2902 units |
| Average unit price | $0.3 million |
Technical specifications
| Version: 500U Shrike Commander | |
|---|---|
| Operational range | 1,735 km (1,078 mi) |
| Wing area | 24 m² (258.3 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 15.0 m (49.0 ft) |
| Height | 4.4 m (14.5 ft) |
| Length | 11.2 m (36.8 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 5,913 m (19,400 ft) |
| Empty weight | 2,102 kg (4,634 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 3,062 kg (6,751 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 6.8 m/s (22.3 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x radial engine Lycoming IO-540-E1B5 delivering 216 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Colombia | 6 | |

|
Mexico | 6 | |

|
Argentina | 3 | |

|
Iran | 3 | |

|
Dominican Republic | 2 | |
|
Pakistan | 2 | |

|
Philippines | 2 | |

|
South Korea | 1 | |

|
Peru | 1 | |
|
Thailand | 1 | |

|
Venezuela | 1 | |
All operators


Description
The Aero Commander 500 family originated in the late 1940s with the Aero Design and Engineering Company, later renamed the Aero Commander company in 1950. The concept for this light business twin was conceived by Ted Smith, an engineer at Douglas Aircraft Company, who, with a group of A-20 engineers, worked part-time to design and build the aircraft with a layout reminiscent of the A-20 bomber. The initial plan involved constructing three pre-production aircraft, but the company later decided to focus on a single prototype, designated the Model L3805, with the final configuration completed in July 1946. The prototype, registered as NX1946, first flew on April 23, 1948, accommodating up to five people and powered by two Lycoming O-435-A piston engines; it featured an all-metal, high-wing monoplane design with retractable undercarriage components sourced from a Vultee BT-13 Valiant. Walter Beech considered buying the project but instead developed the Beechcraft Twin Bonanza. Fairchild Aircraft also evaluated the prototype. The company then leased a factory at Bethany near Oklahoma City to build a production version, certified on June 30, 1950. After nearly 10,000 hours of redesign, the production model, named the Commander 520 and powered by more powerful Lycoming GO-435-C2 engines, was rolled out in August 1951.
The Aero Commander family showcases an all-metal, high-wing monoplane design. This design incorporates a retractable undercarriage utilizing components sourced from a Vultee BT-13 Valiant. The wing profile is based on the NACA 23012 airfoil, with modifications tailored to optimize performance, and the construction features light, durable materials, and accommodates up to eleven seats in the larger variants.
In military service, the Aero Commander was initially designated the L-26, later changed to U-4 for the United States Air Force and U-9 for the United States Army in 1962. One U-4B even served as a presidential transport aircraft for Dwight D. Eisenhower between 1956 and 1960; this aircraft is now owned by the Commemorative Air Force. As of 2004, Shrike Commanders remained in service with the United States Customs Service, United States Coast Guard, and United States Forest Service. A single 560F model was also operated by the Belgian Air Force as the personal transport of King Baudouin of Belgium from 1961 to 1973. The unpressurized, long-fuselage 680FL variant found use as a small package freighter by Combs Freightair in the 1970s and 1980s and by Suburban Air Freight in the 1980s and 1990s.
Main Variants:
-
Commander 520: The initial production version, powered by two Lycoming GO-435-C2 engines with a combined rating of 520 horsepower, could reach speeds of up to 200 mph and accommodate seven seats.
-
500S/Shrike Commander: An improved version of the Aero Commander manufactured after 1967, demonstrated in aerobatic routines.
-
L-26/U-4/U-9: Military designations for the Aero Commander, serving roles in the United States Air Force and United States Army, later redesignated in 1962.
-
Model 695B/Jetprop 1000B: A larger variant with turboprop engines, capable of reaching speeds of up to 330 mph and accommodating 11 seats.
-
Aero Commander 680: A version that experienced accidents, including one involving Senator Ted Kennedy in 1964, and another fatal crash in 1971 that claimed the life of Audie Murphy.