Republic of Korea Air Force
Key facts
| Official Name | Republic of Korea Air Force |
| Local Name | 공군 (Gong-gun) |
| Country | 🇰🇷 South Korea |
| World rank | #7 |
| Active aircraft | 1591 as of 2026 |
| Aircraft on order | 548 |
| Roundel |
|
Global Air Force Index
| 💥 Strategic Bombers | 0 | Nuclear-capable strike aircraft (highest weight) |
| ✈️ Combat Aircraft | 433 | Fighters, multirole & attack aircraft |
| 🚁 Helicopters | 807 | Attack, transport & utility rotorcraft |
| 🛫 Transport | 56 | Strategic & tactical airlift |
| 📊 Total Active | 1592 | All aircraft types |
Methodology: Square root scaled index weighted by aircraft combat capability. Strategic bombers score highest due to nuclear strike capability.
Aircraft by type in 2026
| Aircraft type | Active | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
807 | |
|
|
432 | |
|
|
271 | |
|
|
56 | |
|
|
25 | |
Origin countries of aircraft
| Country | Active Aircraft | |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 1058 | |
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | 450 | |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 32 | |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 18 | |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 18 | |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 15 | |
| 🇫🇷 France | 10 | |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 8 | |
| 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR | 7 | |
| 🇪🇺 Europe | 4 | |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 0 | |
Evolution of South Korean Air Force fleet
1 recent update applied to this inventory
| Date | Aircraft | Active Δ | Ordered Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 Jun 2025 | F-16D | -1 | — |
| F-16D failed to lift off on a Red Flag-Alaska departure, skidded off Eielson’s runway and burned. [Source] | |||
Overview
The Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF) is a technologically advanced and well-equipped force primarily structured to counter the threat posed by North Korea. Organized along US Air Force lines, it is manned by approximately 65,000 personnel. The main operational components are Air Force Operations Command and Air Force Logistics Command, which provide command and control and sustainment for its various assets.
The ROKAF's strategic doctrine is a key component of South Korea's "three-axis system" designed for deterrence and defense against the North. This doctrine includes the "Kill Chain" for preemptive strikes on imminent missile threats, the Korea Air and Missile Defense (KAMD) system for interception, and the Korea Massive Punishment and Retaliation (KMPR) plan, which involves precision strikes to neutralize North Korean leadership in a conflict. While this offensive posture is intended to be defensive, it is a significant shift from previous strategies. The air force's role is critical for deep precision strikes and establishing air superiority to enable this strategy.
Operationally, the ROKAF has focused on developing capabilities for independent deep-strike operations, reducing its historical reliance on US assets. Joint exercises with the United States, such as the large-scale "Ulchi Freedom Shield," enhance interoperability and readiness. In October 2023, the ROKAF participated in its first trilateral exercise with US and Japanese air forces, reflecting an expanding role in regional security.
Significant modernization is underway to replace aging F-4 and F-5 aircraft and to enhance overall capability. A key indigenous program is the development of the KAI KF-21 Boramae, a 4.5-generation fighter aircraft with stealth characteristics, intended to form the future backbone of the fighter fleet. Existing platforms are also being upgraded; the F-15K Slam Eagle fleet is undergoing a major enhancement program to be completed by 2034, which includes AESA radars and advanced electronic warfare suites similar to the F-15EX. The KF-16 fleet is also being modernized to the F-16V configuration with new radars and mission computers, a project expected to be completed by 2025. These modernization efforts are complemented by the acquisition of F-35A stealth fighters to bolster precision strike capabilities against heavily defended targets.
Full inventory in 2026
Republic of Korea Air Force
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-5E | 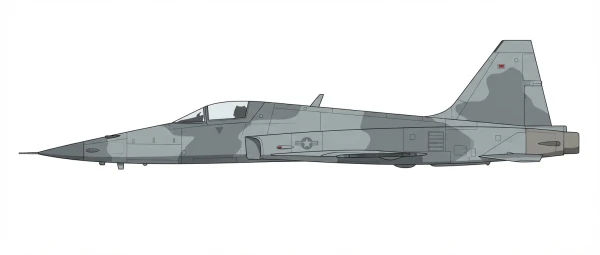 |
🇺🇸 | 1976 | 138 | -15 |
0 |
||
| F-16C |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 118 | 0 |
0 |
||
| F-15K |  |
🇺🇸 | 1986 | 59 | 0 |
0 |
||
| F-16D |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 48 | -1 |
0 |
||
| F-35A |  |
🇺🇸 | 2013 | 40 | 0 |
19 |
||
| F-5F |  |
🇺🇸 | 1965 | 29 | 0 |
0 |
||
| KF-21 |  |
🇰🇷 | 2026 | 0 | 0 |
120 |
||
| MD500 | 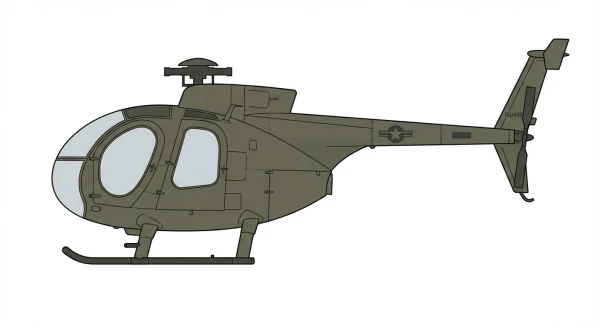 |
🇺🇸 | 1967 | 25 | 0 |
0 |
||
| S-70/HH-60P |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 17 | 0 |
0 |
||
| CH/HH-47D |  |
🇺🇸 | 1962 | 9 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Ka-32 |  |
🇨🇳 | 1982 | 7 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Bell 412 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1959 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| H215M/AS332 |  |
🇩🇪 🇫🇷 | 1978 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
||
| CN235 |  |
🇪🇸 🇮🇩 | 1988 | 18 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C-130H/MC-130K | 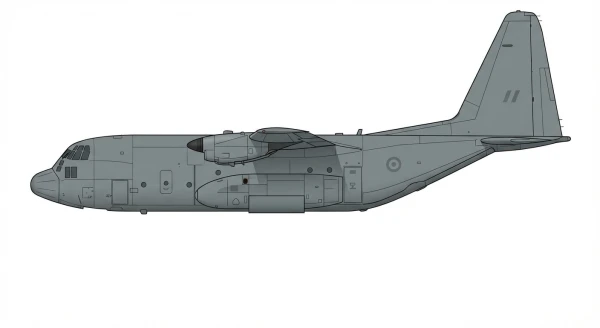 |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 12 | 0 |
0 |
||
| 737 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1968 | 4 | 0 |
0 |
||
| A330 MRTT |  |
🇪🇺 | 1994 | 4 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C-130J |  |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 4 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Falcon 2000/LXS | 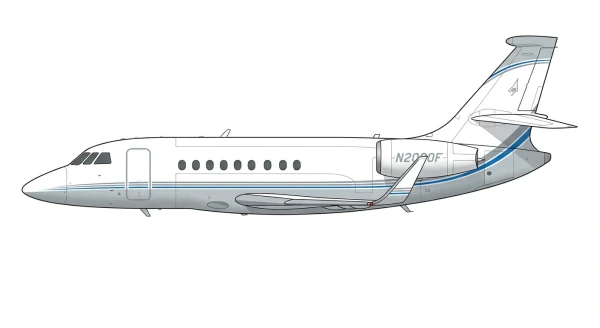 |
🇫🇷 | 1995 | 2 | +2 |
4 |
||
| Twin Commander |  |
🇺🇸 | 1952 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C-390 | 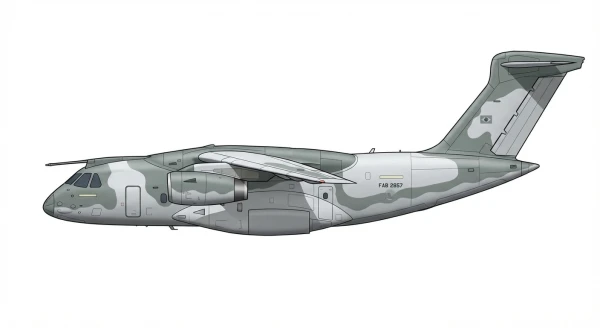 |
🇧🇷 | 2019 | 0 | 0 |
3 |
||
| KA/KT-1 | 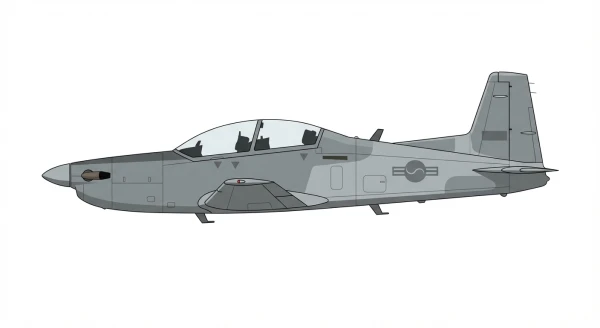 |
🇰🇷 | 2000 | 103 | 0 |
0 |
||
| FA-50 |  |
🇰🇷 | 2005 | 60 | 0 |
0 |
||
| T-50/B |  |
🇰🇷 | 2005 | 60 | 0 |
0 |
||
| TA-50 |  |
🇰🇷 | 2005 | 25 | +3 |
17 |
||
| KT-100 | 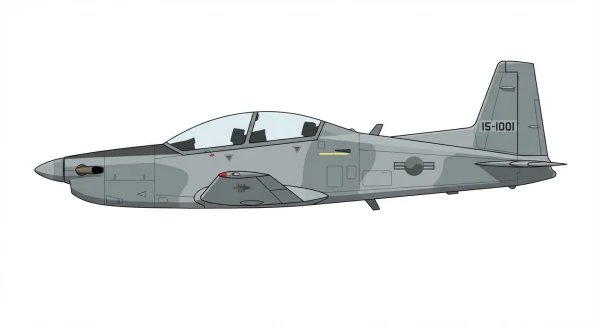 |
🇰🇷 | 2015 | 23 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Hawker 800 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1983 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
Republic of Korea Army
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD500 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1967 | 226 | -20 |
0 |
||
| Surion KUH-1 |  |
🇰🇷 | 2013 | 150 | +50 |
103 |
||
| S-70/UH-60L/P |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 113 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AH-1J/S |  |
🇺🇸 | 1967 | 75 | -1 |
0 |
||
| AH-64E |  |
🇺🇸 | 1984 | 36 | 0 |
36 |
||
| CH-47D/F |  |
🇺🇸 | 1962 | 34 | 0 |
18 |
||
| Bell 505 |  |
🇺🇸 | 2017 | 24 | +24 |
16 |
||
| BO105 |  |
🇩🇪 | 1970 | 12 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Light Attack Helicopter |  |
🇫🇷 | 1999 | 0 | 0 |
200 |
||
| King Air 90 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1964 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
Republic of Korea Marine Corps
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surion MUH-1 |  |
🇰🇷 | 2013 | 29 | 0 |
0 |
Republic of Korea Navy
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lynx 99/A |  |
🇬🇧 | 1978 | 24 | 0 |
0 |
||
| S-70/MH-60R/UH-60P |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 9 | 0 |
12 |
||
| AW159 |  |
🇬🇧 🇮🇹 | 2014 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Bell 505 |  |
🇺🇸 | 2017 | 3 | +3 |
0 |
||
| 737 (P-8A) |  |
🇺🇸 | 1968 | 6 | +3 |
0 |
||
| F406 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1985 | 5 | 0 |
0 |
||
| P-3C/CK |  |
🇺🇸 | 1962 | 16 | 0 |
0 |
Frequently Asked Questions
How many aircraft does South Korea have?
How does South Korea's air force rank globally?
How many combat aircraft does South Korea operate?
How many military helicopters does South Korea have?
What is the Air Force Index of South Korea?
Where does South Korea get its military aircraft from?
Last updated on 23 June 2025. Suggest a change
