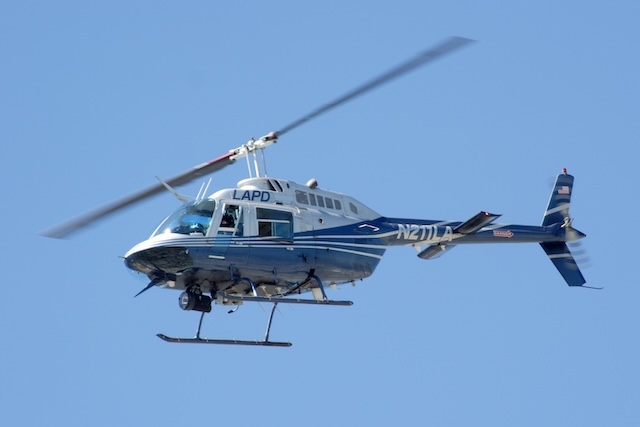
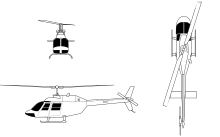
Bell 206 JetRanger
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Bell |
| First flight | 10 January 1966 |
| Year introduced | 1967 |
| Number produced | 7300 units |
| Average unit price | $1.3 million |
Description
The Bell 206 family originated from a United States Navy request on behalf of the Army for a Light Observation Helicopter (LOH). Bell responded with the D-250 design, later designated YHO-4. This initial design was not selected in the competition. Undeterred, Bell redesigned the airframe, leading to the Bell 206A JetRanger. This redesign increased cargo space by extending the fuselage and implemented a more aesthetically pleasing design. The Bell 206A received FAA certification in October 1966, with deliveries commencing in January 1967. Bell Helicopter ceased production of the Bell 206B-3 version in 2010.
The Bell 206 family is characterized by its two-bladed main rotor and a compact, streamlined fuselage. The LongRanger variant features a stretched fuselage designed to accommodate seven seats. The 206B-3 model includes an upgraded Allison 250-C20J engine and an increase in the tail rotor diameter by 2 inches (51 mm) for enhanced yaw control.
Details regarding specific armament fitments vary by operator. The Hkp 6A, a Swedish Army designation for the Agusta-Bell 206A, was utilized as an anti-tank helicopter, armed with Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGMs). Additionally, the Hkp 6B, a Swedish Navy designation for the Agusta-Bell 206A, was employed as an anti-submarine helicopter, equipped with depth charges.
The Bell 206 family has seen extensive operational use across various sectors. The United States Navy adopted the 206A in 1968, designating it the TH-57 Sea Ranger for training helicopter pilots. The U.S. Army selected it for light observation duties as the OH-58 Kiowa. The JetRanger is employed by news media for traffic and news reporting. The LongRanger is commonly used for air ambulance services and corporate transport. The Canadian market quickly adopted the Bell 206B shortly after its certification in 1967, particularly within resource industries like oil and gas exploration, mining, and forestry, leveraging its adaptability to harsh environments.
Main Variants:
-
Bell 206A: The initial production version, powered by an Allison 250-C18 turboshaft engine, was FAA-certified in 1966 and later selected as the OH-58A Kiowa in 1968.
-
Bell 206B: This variant featured an upgraded Allison 250-C20 engine, enhancing its performance capabilities.
-
Bell 206B-3: This model incorporated an upgraded Allison 250-C20J engine and a tail rotor diameter increased by 2 inches (51 mm) to improve yaw control.
-
Bell 206L LongRanger: A stretched, seven-seat configuration, it was powered by an Allison 250-C20B turboshaft engine, offering increased passenger capacity.
-
Bell 206LT TwinRanger: This twin-engined variant of the 206L, available as conversions and new-builds, was eventually replaced by the Bell 427 in Bell's product lineup.
Technical specifications
| Version: OH-58D Kiowa Warrior | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 2 members |
| Maximum speed | 240 km/h (149 mph) |
| Height | 3.9 m (12.9 ft) |
| Length | 12.9 m (42.2 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 4,572 m (15,000 ft) |
| Empty weight | 1,737 kg (3,829 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 2,495 kg (5,501 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 1 x turbomoteur Allison 250-C30 delivering 485 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 113 | |

|
Iraq | 69 | |

|
Greece | 68 | |

|
Taiwan | 66 | |

|
Colombia | 47 | |

|
United Arab Emirates | 43 | |

|
Mexico | 41 | |
|
Italy | 29 | |
|
Croatia | 23 | |

|
Dominican Republic | 22 | |

|
Israel | 22 | |

|
Turkey | 22 | |
|
Thailand | 20 | |
|
Pakistan | 18 | |

|
Tunisia | 18 | |

|
Saudi Arabia | 15 | |

|
Argentina | 13 (+5) | |

|
Canada | 13 | |

|
Austria | 10 | |

|
Brazil | 10 | |
|
Bangladesh | 9 | |

|
Ecuador | 7 | |
|
Bulgaria | 6 | |

|
Germany | 6 | |

|
Iran | 6 | |

|
Morocco | 6 | |

|
Chile | 5 | |

|
Guatemala | 5 | |

|
Sri Lanka | 5 | |

|
Uganda | 5 | |

|
Venezuela | 5 | |
|
North Macedonia | 4 | |

|
Oman | 4 | |

|
Slovenia | 4 | |

|
Albania | 3 | |

|
Myanmar | 3 | |

|
Brunei | 2 | |
| 🇨🇩 | Congo Democratic Republic | 2 | |

|
Peru | 2 | |
|
Zambia | 2 | |

|
Cameroon | 1 | |
| 🇬🇶 | Equatorial Guinea | 1 | |
|
Guyana | 1 | |

|
Nicaragua | 1 | |

|
Panama | 1 | |

|
Senegal | 1 | |

|
Yemen | 1 | |
All operators
Armament
Missiles payload:
- Air-to-Air Short-Range General Dynamics AIM-92 Stinger
- Anti-Tank Lockheed-Martin AGM-114 Hellfire
- Air-to-Surface Raytheon AGM-176 Griffin